[dropcap style=”font-size:100px; color:#992211;”]O[/dropcap]ne area where cultural fusion works particularly well is music.
It is a universal language that spans the limitations of geography, heritage and time. Ignoring the most pretentious of musical snobs and purists, for most people born post-WW2, rock music is what they were raised on. Along with blues and jazz, it is possibly the greatest contribution to modern culture the US has made.
Our voices, and drums, are our most primordial means of communication, and listening to the Buffalo Hat Singers, you can feel that right to the core of your being. For me, if music doesn’t have live drumming it is lacking its heart and soul. Of course, a great voice accompanied by a solo guitar also works.
Music has become a vital and integral part of the festival, and through the free concerts in Place des Festivals, it is now the most popular part. The fact that Présence Autochtone coincides with Osheaga, now Canada’s biggest music festival (happening a short Metro ride away) hasn’t dampened enthusiasm. If Osheaga is Glastonbury, then this is WOMAD. The “world music” aspect was further highlighted this year through the festival’s collaboration with Vive 375, a year-long celebration of Montreal’s 375th anniversary.
Présence Autochtone is not only a celebration of the aboriginal heritage of Canada and the Americas, but the indigenous people around the world who have suffered at the hands of European Christians and imperialists. The festival’s annual parade and presentation has always celebrated the city’s diverse cultures, which make it the vibrant place it is, which is especially evident during the balmy summer months.
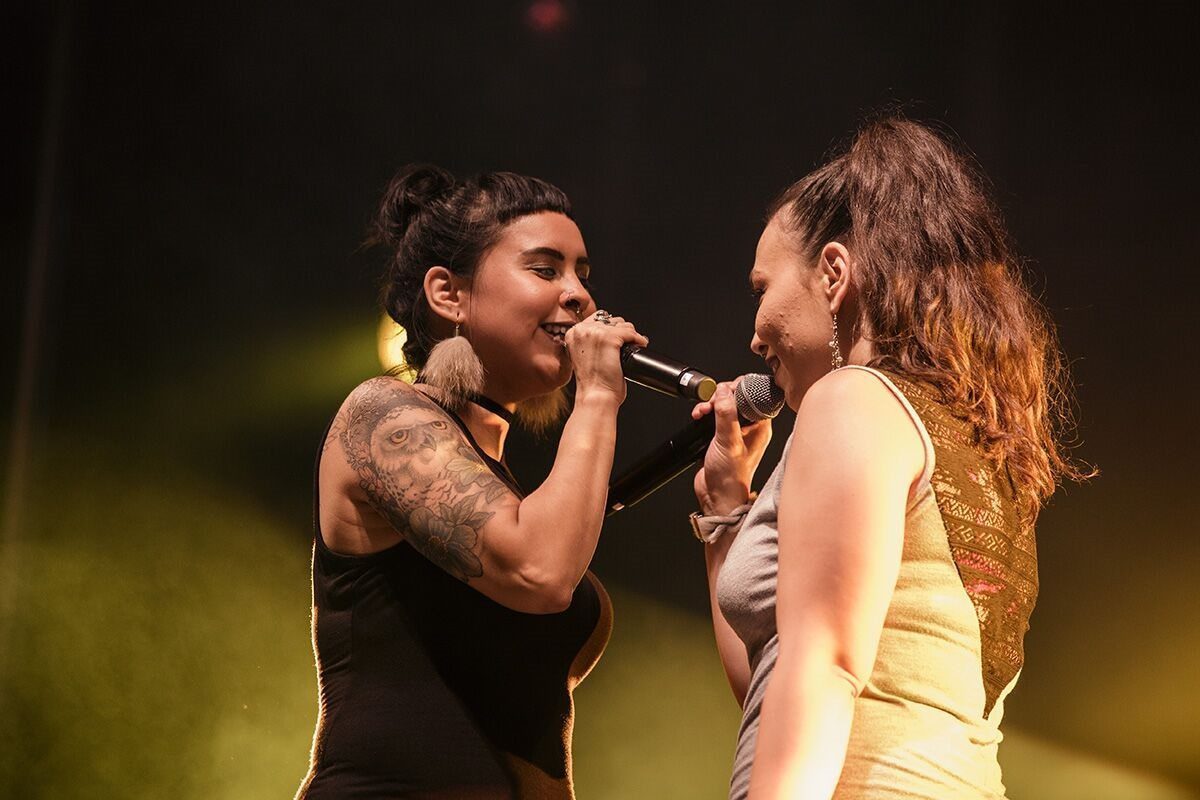

Thursday evening saw Silla + Rise (pictured, above) performing a fascinating mix of Inuit throat singing combined with electronic beats. Some of the songs were freeform, like hip-hop or even jazz scatting. A rather fascinating and unique sound.
Like the previously mentioned Wapikoni, Musique Nomade is an initiative for indigenous musicians to record, promote and distribute their music. The music available is as diverse as the nations it comes from, and with a multitude of influences. This was perfectly displayed at Nikamotan MTL, a showcase of Musique Nomade artists that featured individual performances and duets, embracing styles from blues to hip-hop to country to reggae.
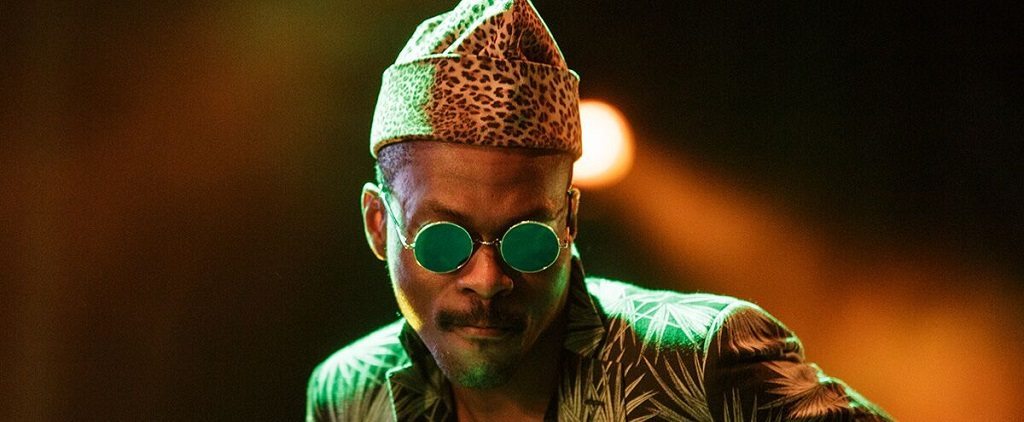
This musical cross-pollination continued on the Saturday evening with Nova Stella, which incorporated a panoply of musicians and spoken-word artists from across the city’s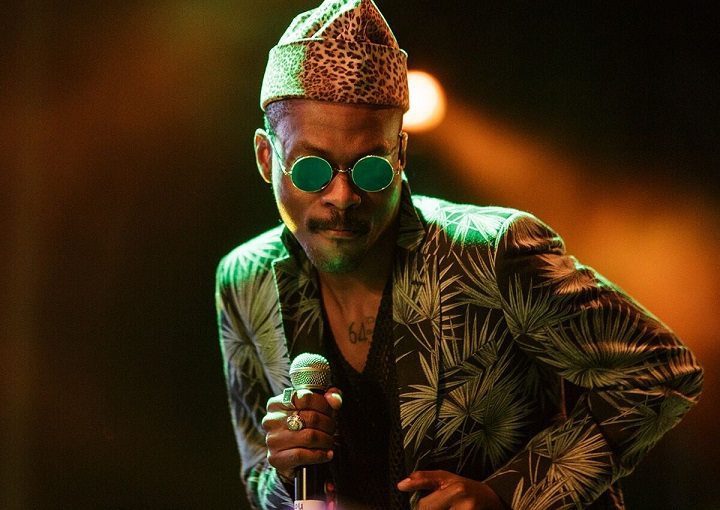 émigré communities. As with the previous night’s Nikamotan MTL, there were duets from unlikely pairings of diverse performers. Rap and hip-hop were fairly predominant, but the highlights were Congolese singer Pierre Kwenders, (pictured, right) who mixes rumba with electronic beats and a riveting stage presence; Shauit, a regular at the festival, performed original reggae songs in his native Innu tongue; and Nomadic Massive, an international collective of musicians whose upbeat mix of primarily hip-hop and soul, proved to be a crowd-pleasing finale to the evening.
émigré communities. As with the previous night’s Nikamotan MTL, there were duets from unlikely pairings of diverse performers. Rap and hip-hop were fairly predominant, but the highlights were Congolese singer Pierre Kwenders, (pictured, right) who mixes rumba with electronic beats and a riveting stage presence; Shauit, a regular at the festival, performed original reggae songs in his native Innu tongue; and Nomadic Massive, an international collective of musicians whose upbeat mix of primarily hip-hop and soul, proved to be a crowd-pleasing finale to the evening.
The importance of First Nation people’s contribution to contemporary music was further underlined in the closing night film Rumble: The Indians Who Rocked the World. The film’s title comes from the classic instrumental by Link Wray, who was a native American. Released in 1958 it was a groundbreaking guitar tune that predates the current garage and surf rock by 50 years, and was a major influence on the world’s great rock guitarists such as Led Zeppelin’s Jimmy Page. Despite this, Wray’s heritage was unknown or hidden from the general public.
As previously stated, contemporary (20th century) American music, which encompasses jazz, blues, folk and rock, is arguably the nation’s greatest contribution to world culture, and for the most part is attributed to African-Americans, but this film reveals that the First Nations’ people played a far more influential role than is generally known. Part of this is due to the fact that the Indians were even more marginalised and persecuted than blacks, and their story suppressed (in much the same way as the genocide of Roma/Sinti in Nazi Germany was). The film investigates the cross-pollination of Afro-American and First Nations’ people, both physically and culturally. Jimi Hendrix is undoubtedly one of the most famous sons. The film also looks at other influential artists such as blues singer Charley Patton, jazz singer Mildred Bailey, the aforementioned rock guitarists Link Wray, protest folk singer Buffy Sainte-Marie (who became a victim of a CIA/FBI witch hunt), The Band’s Robbie Robertson, as well as the tragic story of prodigious guitarist Jesse Ed Davies. The film also interviews many luminaries from the music world who all attest to the important contributions and influence of these musicians, and the music of the indigenous people in general.
This is a brilliant, eye-opening documentary that adds a vital chapter to the origins of modern music, and served as fitting coda to the festival that had been celebrating the universality of music, as well as highlighting, through its film programming, the ongoing struggles, and triumphs, of aboriginal people throughout North America and the rest of the world.
Should you ever find yourself in Montreal in the summer months, possibly to take in the plethora of high-profile festivals, take time out to explore the offerings of Présence Autochtone, with its free music concerts and thought-provoking films.
Read part one of this review here.
Chris Patmore is a photographer-designer-writer in order of creative satisfaction, or a designer-writer-photographer in order of current earnings. After becoming totally disillusioned with the world of film journalism he has returned to his first loves: music and photography. Sirius Flatz, manager of Molotov Jukebox, says, “Chris has what one could call a musical eye, capturing bands in their perfect moments.”