[dropcap style=”font-size:100px; color:#992211;”]W[/dropcap]eird physics, electricity, heat.
Get stuff, burn stuff, make warm. Warm good. Like warm. Mmm.
Thermionic Conversion
Through a process known as thermionic conversion, heat energy — such as light from the sun or heat from burned fossil fuels — can be converted into electricity with very high efficiency. Because of its promise, researchers have been trying for more than half a century to develop a practical thermionic generator, with little luck. That luck may soon change, thanks to a new design — dubbed a thermoelectronic generator — described in AIP Publishing’s Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy (JRSE).
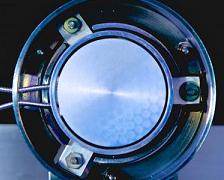
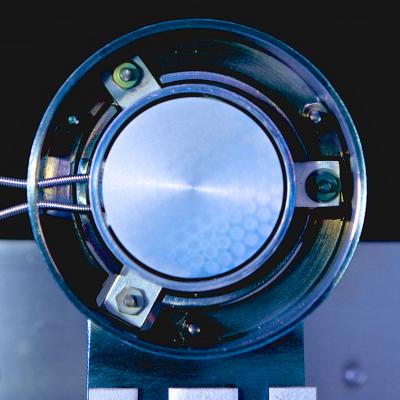 This is a view into the test generator, looking at the emitter (~ 3 cm diameter).
This is a view into the test generator, looking at the emitter (~ 3 cm diameter).
Thermionic generators use the temperature difference between a hot and a cold metallic plate to create electricity. “Electrons are evaporated or kicked out by light from the hot plate, then driven to the cold plate, where they condense,” explained experimental solid-state physicist Jochen Mannhart of the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research in Stuttgart, Germany (the lead author of the JRSE paper).
Without moving mechanical parts
The resulting charge difference between the two plates yields a voltage that, in turn, drives an electric current, “without moving mechanical parts,” he said.
Previous models of thermionic generators have proven ineffectual because of what is known as the “space-charge problem,” in which the negative charges of the cloud of electrons leaving the hot plate repel other electrons from leaving it too, effectively killing the current.
Mannhart, along with his former students Stefan Meir and Cyril Stephanos, and colleague Theodore Geballe of Stanford University, circumvented this problem using an electric field to pull the charge cloud away from the hot plate, which allowed electrons to fly to the cold plate.
Commercial Application
“Practical thermionic generators have reached efficiencies of about 10 percent. The theoretical predictions for our thermoelectronic generators reach about 40 percent, although this is theory only,” noted Mannhart. “We would be much surprised if there was a commercial application in the marketplace within the next five years, but if companies that are hungry for power recognize the potential of the generators, the development might be faster.”
Source: American Institute of Physics
Photo: J.Mannhart/MPG.de

Some of the news that we find inspiring, diverting, wrong or so very right.