[dropcap style=”font-size:100px; color:#992211;”]P[/dropcap]
arisian kids coughing up nanotubes, and it’s not the Gauloises.
Tinfoil hats at the ready, monsieurs et madames, there’s something spooky going on.
Cars appear to produce carbon nanotubes, and some of the evidence has been found in human lungs.
Rice University scientists working with colleagues in France have detected the presence of man-made carbon nanotubes in cells extracted from the airways of Parisian children under routine treatment for asthma. Further investigation found similar nanotubes in samples from the exhaust pipes of Paris vehicles and in dust gathered from various places around the city.
The researchers reported in the journal EBioMedicine this month that these samples align with what has been found elsewhere, including Rice’s home city of Houston, in spider webs in India and in ice cores.
The research in no way ascribes the children’s conditions to the nanotubes, said Rice chemist Lon Wilson, a corresponding author of the new paper. But the nanotubes’ apparent ubiquity should be the focus of further investigation, he said.
“We know that carbon nanoparticles are found in nature,” Wilson said, noting that round fullerene molecules like those discovered at Rice are commonly produced by volcanoes, forest fires and other combustion of carbon materials. “All you need is a little catalysis to make carbon nanotubes instead of fullerenes.”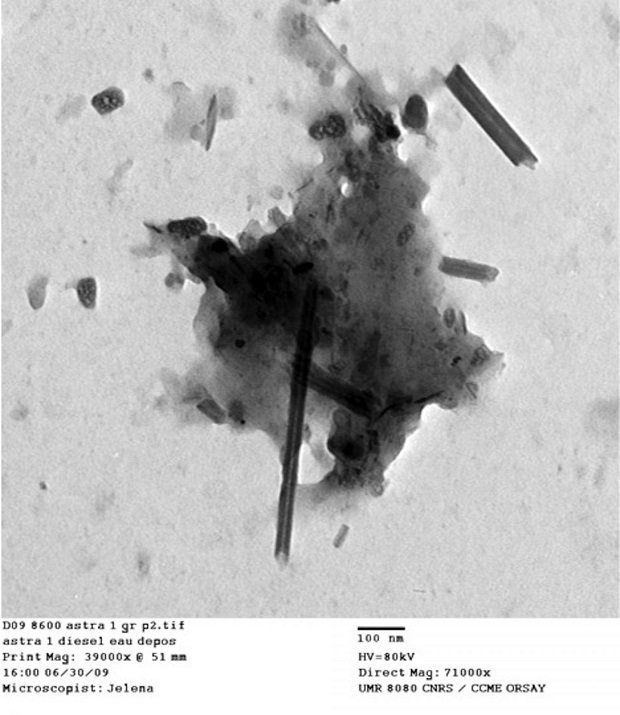
A car’s catalytic converter, which turns toxic carbon monoxide into safer emissions, bears at least a passing resemblance to the Rice-invented high-pressure carbon monoxide, or HiPco, process to make carbon nanotubes, he said. “So it is not a big surprise, when you think about it,” Wilson said.
The team led by Wilson, Fathi Moussa of Paris-Saclay University and lead author Jelena Kolosnjaj-Tabi, a graduate student at Paris-Saclay, analyzed particulate matter found in the alveolar macrophage cells (also known as dust cells) that help stop foreign materials like particles and bacteria from entering the lungs.
The researchers wrote that their results “suggest humans are routinely exposed” to carbon nanotubes. They also suggested previous studies that link the carbon content of airway macrophages and the decline of lung function should be reconsidered in light of the new findings. Moussa confirmed his lab will continue to study the impact of man-made nanotubes on health.
The cells were taken from 69 randomly selected asthma patients aged 2 to 17 who underwent routine fiber-optic bronchoscopies as part of their treatment. For ethical reasons, no cells from healthy patients were analyzed, but because nanotubes were found in all of the samples, the study led the researchers to conclude that carbon nanotubes are likely to be found in everybody.
The study notes but does not make definitive conclusions about the controversial proposition that carbon nanotube fibers may act like asbestos, a proven carcinogen. But the authors reminded that “long carbon nanotubes and large aggregates of short ones can induce a granulomatous (inflammation) reaction.”
The study partially answers the question of what makes up the black material inside alveolar macrophages, the original focus of the study. The researchers found single-walled and multiwalled carbon nanotubes and amorphous carbon among the cells, as well as in samples swabbed from the tailpipes of cars in Paris and dust from various buildings in and around the city.
“The concentrations of nanotubes are so low in these samples that it’s hard to believe they would cause asthma, but you never know,” Wilson said. “What surprised me the most was that carbon nanotubes were the major component of the carbonaceous pollution we found in the samples.”
The nanotube aggregates in the cells ranged in size from 10 to 60 nanometers in diameter and up to several hundred nanometers in length, small enough that optical microscopes would not have been able to identify them in samples from former patients. The new study used more sophisticated tools, including high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, X-ray spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and near-infrared fluorescence microscopy to definitively identify them in the cells and in the environmental samples.
“We collected samples from the exhaust pipes of cars in Paris as well as from busy and non-busy intersections there and found the same type of structures as in the human samples,” Wilson said.
“It’s kind of ironic. In our laboratory, working with carbon nanotubes, we wear facemasks to prevent exactly what we’re seeing in these samples, yet everyone walking around out there in the world probably has at least a small concentration of carbon nanotubes in their lungs,” he said.
The researchers also suggested that the large surface areas of nanotubes and their ability to adhere to substances may make them effective carriers for other pollutants.
The study followed one released by Rice and Baylor College of Medicine earlier this month with the similar goal of analyzing the black substance found in the lungs of smokers who died of emphysema. That study found carbon black nanoparticles that were the product of the incomplete combustion of such organic material as tobacco.
Source: Eurekalert/Rice University
Photo: Fathi Moussa/Paris-Saclay University

Some of the news that we find inspiring, diverting, wrong or so very right.




















